Secondary Treatment: Further treatment of the water by removing remaining larger solids and working on metabolizing organic matter. It is usually comprised of trickling filters, aeration tanks, and clarifiers (similar to sedimentation tanks).
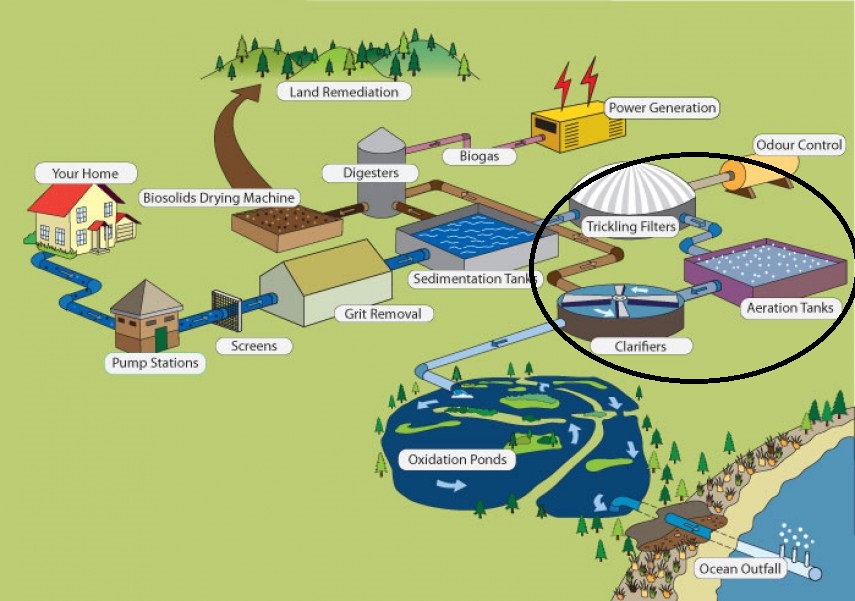
Aeration: A part of the secondary treatment process where air is added to the water to encourage microbe growth (by mixers or blowers). The microbes then feed on the organic matter and it flocculates and settles to the bottom.
Aerobic: Microorganisms or processes that require oxygen.
Anaerobic: Microorganisms or processes that do not need/want oxygen.
Blower: Used in the aeration process to increase the dissolved oxygen levels. They can also be used for air scouring and digester gas.
Dissolved Oxygen: The measure of how much oxygen is dissolved in the water, also known as DO.
Flocculates: The process of many small particles clumping together to form a larger solid, also known as a floc.
Membrane Filter: Filters with micropores that water is pushed through to remove smaller particles. Dissolved components may get through. Sometimes membrane filters are used with blowers to help aerate water with smaller bubbles.
Trickling Filter: Used to remove organic matter from wastewater using aerobic microorganisms attached to a medium. Common in packed bed reactors (bio-towers). Normally known as attached-growth processes, but if microorganisms are in liquid it is called suspended-growth processes.