Upon completion of this module analysts should be able to successfully obtain data from visual inspection of a motor and motor nameplate in order to characterize the motor.
The motor nameplate is located on the motor itself usually in a location where personnel can read it. You may need permission to access the motor nameplate. Ask the facility contact if you can have someone escort you to the motor, or ask if it is ok to go there alone. You may need the following tools while accessing the nameplate: Ladder, Camera(Phone), and a brush. It should be noted that there are inherent safety risks when accessing motor nameplates. Refer to the Industrial Assessment Safety chapter.
The information typically found on the motor nameplate includes the following:
The following information may also be included
Sometimes this is indicated with the Greek letter ϕ, or with the abbreviation "PH". Example: 3 phase is represented by 3ϕ.
Make a note if motor is vertical shaft, due to extra costs (standard horizontal motors cannot be mounted vertically since different bearings are needed).

TEFC - Totally Enclosed Fan Cooled
This type of enclosure is more common in environments with contaminants (dust, humidity, drips, etc.) that could harm the motor.
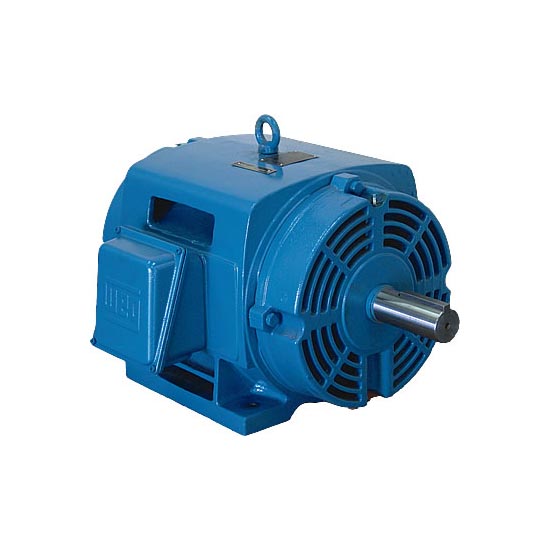

ODP - Open Drip Proof
This enclosure type is open to the environment and should not be used in high contaminant facilities however these motors typically have laminated windings and sealed bearings to protect against contaminants. They tend to be more efficienct than TEFC motors because of the open cooling.
Direct drive - This means no reduction from gears (no belts,chains, etc.)

High torque drive belt - Looks similar to car timing belt

Standard v-belt - These belts are wider in the external perimeter. The next is a cross-sectional diagram of a standard v-belt.
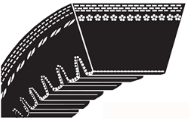
Notched v-belt - These belts are a combination of high-torque belts and v-belts. Compared to the previous 2 belts, the advantage of this type is that it takes less energy to bend due to the notches.
Gearbox - on occasion, equipment might be connected to motors via a gear box that might reduce or increase the RPM.

Here is a video explaining some nameplate basics.
References
"ODP High Efficiency Motors - NEMA Standard - Electric Motors - Products & Services - Belgium - WEG." Change. N.p., n.d. Web. 15 May 2017.
V-Belts;Power Transmission Belts;Synchronous Belts;Timing Belts;Industrial V-Belts;Low Cost;Discount Prices. N.p., n.d. Web. 15 May 2017.
"Margot Machinery: A Used Converting, Paper, Plastics, And Nonwovens Machinery And Equipment Dealer." Used Machinery for the Converting, Paper, Plastics & Nonwovens Industries - Margot Machinery. N.p., n.d. Web. 15 May 2017.